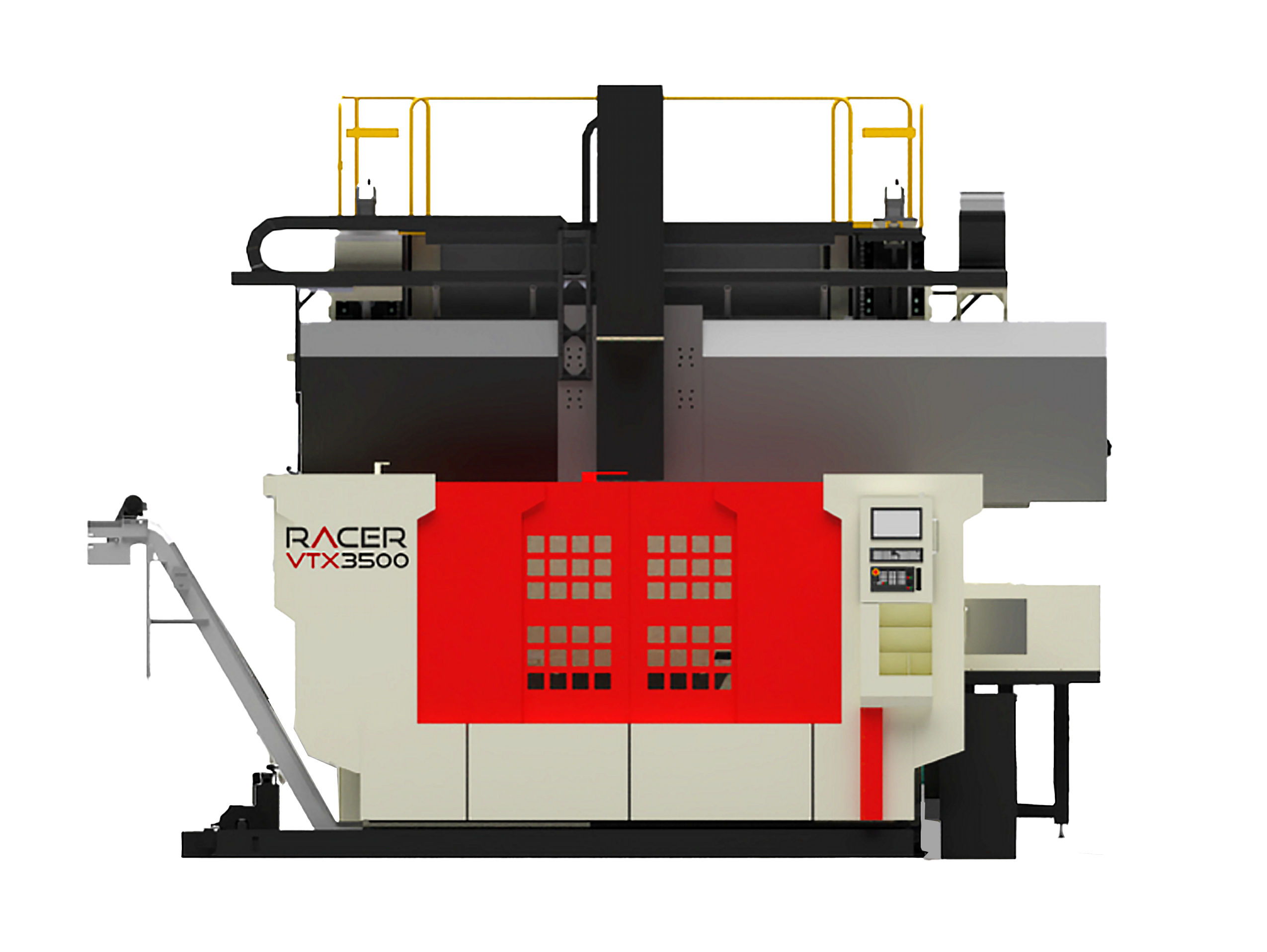
Our Machines
Company Profile
Racer Machinery International Inc. (RACER) manufactures innovative turnkey solution CNC machine tools, metal cutting engine lathes and industrial saws providing high-quality North American built products to production operations worldwide.
Company Profile Working With Racer
Our vision is to be the world leader in machine tool products, providing our customers with high-quality North American built machinery and creative solutions that will allow their companies’ to prosper while contributing to the local economy.
100+ years of experience
All machines are built locally from the ground up
Only engine lathe manufacturer in North America
Innovative designs
Research-based approach
Racer Figures
19980+
Worldwide Installation
60
Year Machine Longevity
Year Machine Longevity
1931
Company History Dating Back To
Industry Solutions

The Phantom Machine Technology™ Advantage
CNC controlled and TURNKEY solution based OEM machine tools built with state-of-the-art patented technology that redefines the machine tool industry and breaks a nearly two-hundred year old tradition - an evolution that’s setting new global benchmarks.
- Dramatically reduced machining time
- Astounding cutting performance
- Versatility in performance